PHP MySQL
Connecting to MySQL Database
Summary:
Before connecting to a MySQL database, you have to specify the following information:
specifies the address of the MySQL database server.
You can use IP address or server name e.g., 127.0.0.1 or localhost
MySQL database name: indicates the name of the database to which you want to connect.
Username and password: specify username and password of the MySQL's user that you use to connect to the MySQL database server.
The account must have sufficient privileges to access the database specified above.
We will use:
The local MySQL database server so the DSN is localhost .
The classicmodels as the sample database.
The root account with a blank password, just for the sake of demonstration.
Connecting to MySQL steps
First, to make it convenient, we will create a new PHP file for database configuration named dbconfig.php that holds all configured parameters:
<?php
$host = 'localhost';
$dbname = 'classicmodels';
$username = 'root';
$password = '';
Second, we create a new PHP file named phpmysqlconnect.php :
<?php
require_once 'dbconfig.php';
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
echo "Connected to $dbname at $host successfully.";
} catch (PDOException $pe) {
die("Could not connect to the database $dbname :" . $pe->getMessage());
}
How the script works.
We included the dbconfig.php file into the script by using the require_once function.
Inside the try block, we created a new PDO object with three arguments: connection string, username, and password. The connection string is composed of $host and $dbname variables in the dbconfig.php file.
If the connection to the MySQL database established successfully, we displayed a success message. If there was any errors or exceptions, PHP issued a PDOException that contains the detailed error message. We call the getMesage() method of the PDOException object to get the detailed message for display.
Third, let's test the script from the web browser.
 It works as expected. We've successfully connected to the MySQL server.
Let's try to change something in the code to make the script display an error message. If you set the
It works as expected. We've successfully connected to the MySQL server.
Let's try to change something in the code to make the script display an error message. If you set the $username variable to blank, you will get the following error message:
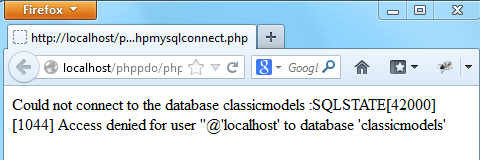 The error message shows that:
Access denied for user ''@'localhost' to database 'classicmodels'
because we don't have any blank user in the
The error message shows that:
Access denied for user ''@'localhost' to database 'classicmodels'
because we don't have any blank user in the classicmodels database.
When the script ends, PHP automatically closes the connection to the MySQL database server. If you want to explicitly close the database connection, you need to set the PDO object to null as follows:
$conn = null;
You can download the scripts of this tutorial via the following download link:
PHP MySQL Connect
In this tutorial, you've learned how to connect to MySQL using PHP PDO object and handle any exception that may occur when connecting the MySQL database.
Create A New Table
Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to use PHP to create MySQL database table by using PDO API.
The following are the steps to show you how to create a new table in a database:
Open a database connection to the MySQL database server.
Execute the
CREATE TABLE statement to create new tables.
Create table example
We will create a new table named tasks in the
sample database with the following SQL script:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
task_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
subject VARCHAR (255) DEFAULT NULL,
start_date DATE DEFAULT NULL,
end_date DATE DEFAULT NULL,
description VARCHAR (400) DEFAULT NULL
);
First, we create a class named CreateTableDemo that has DB configuration parameters. In the constructor of the CreateTableDemo class, we open a connection to the sample database by instantiating a new PDO object.
<?php
/**
* PHP MySQL Create Table Demo
*/
class CreateTableDemo {
/*** database host */
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
/*database name*/
const DB_NAME = 'classicmodels';
/*database user*/
const DB_USER = 'root';
/*database password*/
const DB_PASSWORD = '';
/**@var type */
private $pdo = null;
/*Open the database connection*/
public function __construct() {
// open database connection
$conStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($conStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
}
//...
}
Next, in the destructor of the CreateTabledemo class, we close the database connection by assigning it the null value.
/*close the database connection*/
public function __destruct() {
// close the database connection
$this->pdo = null;
}
Then, define the createTaskTable() method to create the tasks table:
/*create the tasks table
* @return boolean returns true on success or false on failure*/
public function createTaskTable() {
$sql = <<<EOSQL
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
task_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
subject VARCHAR (255) DEFAULT NULL,
start_date DATE DEFAULT NULL,
end_date DATE DEFAULT NULL,
description VARCHAR (400) DEFAULT NULL
);
EOSQL;
return $this->pdo->exec($sql);
}
To execute an SQL statement, you call the exec() method of the PDO object. After that, you can create an instance of the CreateTableDemo class and call the createTaskTable() method.
// create the tasks table
$obj = new CreateTableDemo();
$obj->createTaskTable();
Finally, you can check the classicmodels sample database to see if the tasks table has been created.

 You can download the PHP script file via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Create Table Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you step by step how to use PDO object to create a table in the MySQL database.
Was this tutorial helpful ?
You can download the PHP script file via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Create Table Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you step by step how to use PDO object to create a table in the MySQL database.
Was this tutorial helpful ?
Querying Data from Database
Summary
in this tutorial, you will learn how to query data from MySQL database by using PHP PDO. You will also learn how to use PDO prepared statement to select data securely.
PHP MySQL Querying data using simple SELECT statement
To query data from the MySQL database, follow the steps below:
First, connect to a MySQL database. Check it out
the connecting to MySQL database using PDO tutorial for detail information.
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
Then, construct a
SELECT statement and execute it by using the query() method of the PDO object.
$sql = 'SELECT lastname, firstname, jobtitle
FROM employees
ORDER BY lastname';
$q = $pdo->query($sql);
The query() method of the PDO object returns a PDOStatement object, or false on failure.
Next, set the PDO::FETCH_ASSOC fetch mode for the PDOStatement object by using the setFetchMode() method. The PDO::FETCH_ASSOC mode instructs the fetch() method to return a result set as an array indexed by column name.
$q->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
After that, fetch each row from the result set until there is no row left by using the fetch() method of the PDOStatement object.
<table class="table table-bordered table-condensed">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Job Title</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<?php while ($r = $q->fetch()): ?>
<tr>
<td><?php echo htmlspecialchars($r['lastname']) ?></td>
<td><?php echo htmlspecialchars($r['firstname']); ?></td>
<td><?php echo htmlspecialchars($r['jobtitle']); ?></td>
</tr>
<?php endwhile; ?>
</tbody>
</table>
Putting it all together.
<?php
require_once 'dbconfig.php';
try {
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$sql = 'SELECT lastname,
firstname,
jobtitle
FROM employees
ORDER BY lastname';
$q = $pdo->query($sql);
$q->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die("Could not connect to the database $dbname :" . $e->getMessage());
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>PHP MySQL Query Data Demo</title>
<link href="css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="css/style.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<h1>Employees</h1>
<table class="table table-bordered table-condensed">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Job Title</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<?php while ($row = $q->fetch()): ?>
<tr>
<td><?php echo htmlspecialchars($row['lastname']) ?></td>
<td><?php echo htmlspecialchars($row['firstname']); ?></td>
<td><?php echo htmlspecialchars($row['jobtitle']); ?></td>
</tr>
<?php endwhile; ?>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</div>
</html>

PHP MySQL Querying data using PDO prepared statement
In practice, we often pass the argument from PHP to the SQL statement e.g., get the employee whose last name ends with son . To do it securely and avoid SQL injection attack, you need to use the PDO prepared statement.
Let's take a look at the following example:
<?php
require_once 'dbconfig.php';
try {
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$sql = 'SELECT lastname,
firstname,
jobtitle
FROM employees
WHERE lastname LIKE ?';
$q = $pdo->prepare($sql);
$q->execute(['%son']);
$q->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
while ($r = $q->fetch()) {
echo sprintf('%s <br/>', $r['lastname']);
}
} catch (PDOException $pe) {
die("Could not connect to the database $dbname :" . $pe->getMessage());
}
How the script works.
First, we use a question mark (?) in the SELECT statement. PDO will replace the question mark in the query by the corresponding argument. The question mark is called positional placeholder.
Next, we call the prepare() method of the PDO object to prepare the SQL statement for the execution.
Then, we execute the statement by calling the execute() method of the PDOStatement object. In addition, we pass an argument as an array to replace the placeholder in the SELECT statement. By doing this, the SELECT statement will be translated as follows:
SELECT lastname,
firstname,
jobtitle
FROM employees
WHERE lastname LIKE '%son';
After that, we set the fetch mode for the PDOStatement object.
Finally, we fetch each row of the result set and display the last name field.
PHP provides you with another way to use placeholders in the prepared statement called named placeholder. The advantages of using the named placeholder are:
More descriptive.
If the SQL statement has multiple placeholders, it is easier pass the arguments to the execute() method.
Let's take a look at the following example:
<?php
require_once 'dbconfig.php';
try {
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$sql = 'SELECT lastname,
firstname,
jobtitle
FROM employees
WHERE lastname LIKE :lname OR
firstname LIKE :fname;';
// prepare statement for execution
$q = $pdo->prepare($sql);
// pass values to the query and execute it
$q->execute([':fname' => 'Le%',
':lname' => '%son']);
$q->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
// print out the result set
while ($r = $q->fetch()) {
echo sprintf('%s <br/>', $r['lastname']);
}
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die("Could not connect to the database $dbname :" . $e->getMessage());
}
The :lname and :fname are the named placeholders. They are substituted by the corresponding argument in the associative array that we pass to the execute method.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to query data from MySQL database using PDO objects.
Insert Data Into a Table
Summary
:
in this tutorial, you will learn how to use PHP PDO to insert data into a MySQL table.
We will use the tasks table that we created in the
PHP MySQL create table tutorial. If you have not yet created the tasks table, please follow the tutorial and create it before going forward with this tutorial.
The following picture illustrates the tasks table:
 To insert data into a table, you follow the steps below:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
MySQL INSERT statement.
Call
To insert data into a table, you follow the steps below:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
MySQL INSERT statement.
Call exec() method of the PDO object.
PHP MySQL Insert data examples
PHP MySQL: insert a new row into a table example
<?php
class InsertDataDemo {
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
const DB_NAME = 'classicmodels';
const DB_USER = 'root';
const DB_PASSWORD = '';
private $pdo = null;
/*Open the database connection*/
public function __construct() {
// open database connection
$conStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($conStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
} catch (PDOException $pe) {
die($pe->getMessage());
}
}
//...
The following example illustrates how to insert a new row into the tasks table.
/*Insert a row into a table
* @return*/
public function insert() {
$sql = "INSERT INTO tasks (
subject,
description,
start_date,
end_date
)
VALUES (
'Learn PHP MySQL Insert Dat',
'PHP MySQL Insert data into a table',
'2013-01-01',
'2013-01-01'
)";
return $this->pdo->exec($sql);
}
We defined the InsertDataDemo class with a constructor that establishes the database connection and a destructor that closes the database connection. Please refer to the
PHP MySQL create table tutorial for the code these methods.
Inside the InsertDataDemo class, we define a the insert method that calls the exec() method of the PDO object to execute the INSERT statement.
The following statement creates an instance of the InsertDataDemo class and calls the insert() method to insert a new row into the tasks table.
$obj = new InsertDataDemo();
$obj->insert();
Let's query the data in the tasks table:
SELECT *
FROM tasks;

PHP MySQL: insert a single row using prepared statement example
To pass values from PHP to SQL statement dynamically and securely, you use the PDO prepared statement.
First, use MySQL statement with named placeholders as follows:
$sql = 'INSERT INTO tasks (
subject,
description,
start_date,
end_date
)
VALUES (
:subject,
:description,
:start_date,
:end_date
);';
The :subject, :description, :startdate and :enddate are called named placeholders.
Second, call the prepare() method of the PDO object to prepare the SQL statement for the execution:
$q = $pdo->prepare($sql);
Third, call the execute() method and pass an array that contains the values which are corresponding to the named placeholders.
$q->execute($task)
Putting it all together.
/*Insert a new task into the tasks table
* @param string $subject
* @param string $description
* @param string $startDate
* @param string $endDate
* @return mixed returns false on failure */
function insertSingleRow($subject, $description, $startDate, $endDate) {
$task = array(':subject' => $subject,
':description' => $description,
':start_date' => $startDate,
':end_date' => $endDate);
$sql = 'INSERT INTO tasks (
subject,
description,
start_date,
end_date
)
VALUES (
:subject,
:description,
:start_date,
:end_date
);';
$q = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
return $q->execute($task);
}
Now we can pass the task's data to the insertSingleRow() method:
$obj->insertSingleRow('MySQL PHP Insert Tutorial',
'MySQL PHP Insert using prepared statement',
'2013-01-01',
'2013-01-02');
Le'ts check the tasks table:
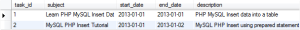
PHP MySQL Insert multiple rows into a table example
There are two ways to insert multiple rows into a table:
Execute the insertSingleRow() method multiple times.
Construct a MySQL INSERT statement that inserts multiple rows and executes it.
Download
You can download the source code of this tutorial via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Insert Source Code
In this tutorial, you have learned how to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP PDO prepared statement.
Update Data
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to update data in a MySQL table using PHP PDO prepared statement.
We are going to use the tasks table in the
sample database for practicing. If you have not yet created the tasks table, please follow the
PHP MySQL create table tutorial to complete it first.
The following picture illustrates the structure of the tasks table.
 To
update data in a table, you use the following steps:
First,
connect to the MySQL database by creating a new PDO object.
Second, construct an
UPDATE statement to update data. If you want to pass values to the
To
update data in a table, you use the following steps:
First,
connect to the MySQL database by creating a new PDO object.
Second, construct an
UPDATE statement to update data. If you want to pass values to the UPDATE statement, you use the named placeholders such as :name.
Third, call the execute() method of the PDOStatement object with an array that contains the corresponding input values of the named placeholders specified in the UPDATE statement.
update data example
PHP MySQL – update a single row
Let's take a look at the following UpdateDataDemo class.
<?php
/**
* PHP MySQL Update data demo
*/
class UpdateDataDemo {
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
const DB_NAME = 'classicmodels';
const DB_USER = 'root';
const DB_PASSWORD = '';
/*PDO instance
* @var PDO*/
private $pdo = null;
/*Open the database connection*/
public function __construct() {
// open database connection
$connStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($connStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die($e->getMessage());
}
}
/*Update an existing task in the tasks table
* @param string $subject
* @param string $description
* @param string $startDate
* @param string $endDate
* @return bool return true on success or false on failure*/
public function update($id, $subject, $description, $startDate, $endDate) {
$task = [
':taskid' => $id,
':subject' => $subject,
':description' => $description,
':start_date' => $startDate,
':end_date' => $endDate];
$sql = 'UPDATE tasks
SET subject = :subject,
start_date = :start_date,
end_date = :end_date,
description = :description
WHERE task_id = :taskid';
$q = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
return $q->execute($task);
}
/*close the database connection*/
public function __destruct() {
// close the database connection
$this->pdo = null;
}
}
$obj = new UpdateDataDemo();
if ($obj->update(2, 'MySQL PHP Update Tutorial',
'MySQL PHP Update using prepared statement',
'2013-01-01',
'2013-01-01') !== false)
echo 'The task has been updated successfully';
else
echo 'Error updated the task';
How the script works.
First, connect to the database by creating a new PDO instance in the constructor of the UpdateDataDemo class.
Second, in the update() method, construct the UPDATE statement with named placeholders.
Third, use a prepared statement to prepare the UPDATE statement for the execution and execute it with an array argument.
you can update a row with id 2 using the following script:
$obj = new UpdateDataDemo();
if($obj->update(2,
'MySQL PHP Update Tutorial',
'MySQL PHP Update using prepared statement',
'2013-01-01',
'2013-01-01') !== false)
echo 'The task has been updated successfully';
else
echo 'Error updated the task';
You can
query data from the tasks table to verify the update:
SELECT *
FROM
tasks;
 You can download the code via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Update Source Code
You can download the code via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Update Source Code
PHP MySQL – update rows in related tables
There are three ways to update rows in related tables:
Use the
MySQL UPDATE JOIN statement.
Use multiple UPDATE statements inside a
transaction.
We will examine the second way in the
PHP MySQL transaction tutorial.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to update data in the MySQL table using the PHP PDO prepared statement.
Delete Data
Summary
:
in this tutorial, you will learn how to delete data from MySQL database table by using PHP PDO.
We will use the tasks table in the
sample database for the demonstration. Before going forward with this tutorial, you should follow the
PHP MySQL create table tutorial to create the tasks table and
insert sample data for practicing.
See the following tasks table.
 To delete data in a table, you use the following steps:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
DELETE statement to delete a row, multiple rows, or all rows in a table. If you want to delete all rows in a big table quickly and more efficiently, you use the
TRUNCATE TABLE statement.
Execute the
To delete data in a table, you use the following steps:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
DELETE statement to delete a row, multiple rows, or all rows in a table. If you want to delete all rows in a big table quickly and more efficiently, you use the
TRUNCATE TABLE statement.
Execute the DELETE statement by calling the exec() method of the PDO object or the execute() method of the PDOStatement object.
PHP MySQL Delete data examples
PHP MySQL: delete a single row example
To delete a single row in a table, you use the DELETE statement with a
WHERE clause that specifies which row to delete.
The following script deletes a row with id 2 in the tasks table.
<?php
/**
* PHP MySQL Delete Data Demo
*/
class DeleteDataDemo {
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
const DB_NAME = 'classicmodels';
const DB_USER = 'root';
const DB_PASSWORD = '';
/*PDO instance
* @var PDO */
private $pdo = null;
/*Open a database connection to MySQL*/
public function __construct() {
// open database connection
$conStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($conStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die($e->getMessage());
}
}
/*Delete a task based on a specified task id
* @param int $id
* @return bool true on success or false on failure*/
public function delete($id) {
$sql = 'DELETE FROM tasks
WHERE task_id = :task_id';
$q = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
return $q->execute([':task_id' => $id]);
}
/*close the database connection*/
public function __destruct() {
$this->pdo = null;
}
}
$obj = new DeleteDataDemo();
// delete id 2
$obj->delete(2);
How it works.
In the __construct() method of the DeleteDataDemo class, we connect to the MySQL database by initiating an instance of the PDO class, and in the __destruct() method, we close the database connection.
The delete() method accepts the id as the argument. First, we call the prepare() method of the PDO object to prepare the DELETE statement for execution, and then we pass an array that contains values corresponding to the named placeholders in the DELETE statement to the execute() method of the PDOStatement object.
To delete the task with id 2, we create an instance of the DeleteDataDemo class and call the delete() method.
PHP MySQL: delete all rows in a table examples
There are two ways to delete all rows in a table:
Issue a DELETE statement without a
WHERE clause.
Issue a TRUNCATE TABLE statement.
The following deleteAll() method deletes all rows in the tasks table using the DELETE statement:
<?php
/**
* Delete all rows in the tasks table
*/
public function deleteAll(){
$sql = 'DELETE FROM tasks';
return $this->pdo->exec($sql);
}
The following truncateTable() method removes all rows in the tasks table as well as resets its
autoincrement column's value:
<?php
/**
* Truncate the tasks table
*/
public function truncateTable() {
$sql = 'TRUNCATE TABLE tasks';
return $this->pdo->exec($sql);
}
You can download the source code of this tutorial via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Delete Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to delete data from MySQL table using PHP PDO.
Call MySQL Stored Procedures
Summary
:
in this tutorial, you will learn how to call MySQL stored procedures using PHP PDO. We will show you how to call stored procedures that return a result set and stored procedures that accept input/output parameters.
Calling stored procedures that return a result set
The steps of calling a
MySQL stored procedure that returns a result set using PHP PDO are similar to
querying data from MySQL database table using the SELECT statement. Instead of sending a SELECT statement to MySQL database, you send a stored procedure call statement.
First, create a stored procedure named GetCustomers() in the
sample database for the demonstration. The GetCustomers()
stored procedure retrieves the name and credit limit of customers from the customers table.
The following GetCustomers() stored procedure illustrates the logic:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomers()
BEGIN
SELECT customerName, creditlimit
FROM customers;
END$$
Second, create a new PHP file named phpmysqlstoredprocedure1.php
with the following code
:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>PHP MySQL Stored Procedure Demo 1</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/table.css" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<?php
require_once 'dbconfig.php';
try {
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// execute the stored procedure
$sql = 'CALL GetCustomers()';
// call the stored procedure
$q = $pdo->query($sql);
$q->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die("Error occurred:" . $e->getMessage());
}
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Customer Name</th>
<th>Credit Limit</th>
</tr>
<?php while ($r = $q->fetch()): ?>
<tr>
<td><?php echo $r['customerName'] ?></td>
<td><?php echo '$' . number_format($r['creditlimit'], 2) ?>
</td>
</tr>
<?php endwhile; ?>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Everything is straightforward except the SQL query:
CALL GetCustomers();
We send the statement that calls the GetCustomers()
stored procedure to MySQL. And we execute the statement to get a result set.
Third, test the script in the web browser to see how it works.
 You can download the script via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Stored Procedure Source Code
You can download the script via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Stored Procedure Source Code
Calling stored procedures with an OUT parameter
It is a little bit tricky to call a stored procedure with the OUT parameter. We will use the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure that accepts a customer number as an input parameter and returns the customer level based on credit limit.
Check the
MySQL IF statement tutorial for detailed information on the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel(
in p_customerNumber int(11),
out p_customerLevel varchar(10))
BEGIN
DECLARE creditlim double;
SELECT creditlimit INTO creditlim
FROM customers
WHERE customerNumber = p_customerNumber;
IF creditlim > 50000 THEN
SET p_customerLevel = 'PLATINUM';
ELSEIF (creditlim <= 50000 AND creditlim >= 10000) THEN
SET p_customerLevel = 'GOLD';
ELSEIF creditlim < 10000 THEN
SET p_customerLevel = 'SILVER';
END IF;
END$$
In MySQL, we can call the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure as follows:
CALL GetCustomerLevel(103,@level);
SELECT @level AS level;
In PHP, we have to emulate those statements:
First, we need to execute the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure.
Second, to get the customer level, we need to query it from the variable @level . It is important that we must call the method closeCursor() of the PDOStatement object in order to execute the next SQL statement.
Let's take a look at how the logic is implemented in the following PHP script:
<?php
require_once 'dbconfig.php';
/**
* Get customer level
* @param int $customerNumber
* @return string
*/
function getCustomerLevel(int $customerNumber) {
try {
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// calling stored procedure command
$sql = 'CALL GetCustomerLevel(:id,@level)';
// prepare for execution of the stored procedure
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
// pass value to the command
$stmt->bindParam(':id', $customerNumber, PDO::PARAM_INT);
// execute the stored procedure
$stmt->execute();
$stmt->closeCursor();
// execute the second query to get customer's level
$row = $pdo->query("SELECT @level AS level")->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
if ($row) {
return $row !== false ? $row['level'] : null;
}
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die("Error occurred:" . $e->getMessage());
}
return null;
}
$customerNo = 103;
echo sprintf('Customer #%d is %s', $customerNo, getCustomerLevel($customerNo));
If you test the script in the web browser, you will see the following screenshot:
 You can download the script via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Stored Procedure with the OUT Parameter Source Code
In this tutorial, you have learned how to call MySQL stored procedures using PHP PDO.
You can download the script via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Stored Procedure with the OUT Parameter Source Code
In this tutorial, you have learned how to call MySQL stored procedures using PHP PDO.
PHP MySQL Transaction
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to handle MySQL transaction in PHP to ensure data integrity of the database.
 A
transaction is a set of inter-dependent SQL statements that needs to execute in all-or-nothing mode. A transaction is successful if all SQL statements executed successfully. A failure of any statement will trigger the system to rollback to the original state to avoid data inconsistency.
A classic example of the transaction is a money transfer transaction from one bank account to another. It requires three steps:
Check the balance of the transferred account to see if the amount is sufficient for the transfer.
If the amount is sufficient, deduct the amount from the balance of the transferred account.
Add the transfer amount to the balance of the receiving account.
If an error occurs in the second step, the third step should not continue. In addition, if an error occurs in the third step, the second step must be reversed. The amounts of both bank accounts are intact in case of failure or adjusted correctly if the transaction is completed successfully.
A
transaction is a set of inter-dependent SQL statements that needs to execute in all-or-nothing mode. A transaction is successful if all SQL statements executed successfully. A failure of any statement will trigger the system to rollback to the original state to avoid data inconsistency.
A classic example of the transaction is a money transfer transaction from one bank account to another. It requires three steps:
Check the balance of the transferred account to see if the amount is sufficient for the transfer.
If the amount is sufficient, deduct the amount from the balance of the transferred account.
Add the transfer amount to the balance of the receiving account.
If an error occurs in the second step, the third step should not continue. In addition, if an error occurs in the third step, the second step must be reversed. The amounts of both bank accounts are intact in case of failure or adjusted correctly if the transaction is completed successfully.
MySQL transaction in PHP
When you use PDO to
create a connection to the database that supports the transaction, the auto-commit mode is set. It means that every query you issue is wrapped inside an implicit transaction.
Notice that not all
storage engines in MySQL support transaction e.g., MyISAM does not support the transaction, however, InnoDB does.
To handle MySQL transaction in PHP, you use the following steps:
Start the transaction by calling the beginTransaction() method of the PDO object.
Place the SQL statements and the commit() method call in a try block.
Rollback the transaction in the catch block by calling the rollBack() method of the PDO object.
PHP MySQL transaction example
We will
create a table named accounts to demonstrate the money transfer between two bank accounts.
First, execute the following statement to create the accounts table:
CREATE TABLE accounts (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL,
amount DECIMAL (19, 4) NOT NULL
);
Second,
insert two rows into the accounts table:
INSERT INTO accounts(name,amount)
VALUES('John',25000),
('Mary',95000);
Third,
query the accounts table:
SELECT *
FROM accounts;
 Let's take a look at the following
Let's take a look at the following TransactionDemo class:
<?php
/**
* PHP MySQL Transaction Demo
*/
class TransactionDemo {
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
const DB_NAME = 'classicmodels';
const DB_USER = 'root';
const DB_PASSWORD = '';
/*Open the database connection*/
public function __construct() {
// open database connection
$conStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($conStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die($e->getMessage());
}
}
/*PDO instance
* @var PDO */
private $pdo = null;
/*Transfer money between two accounts
* @param int $from
* @param int $to
* @param float $amount
* @return true on success or false on failure.*/
public function transfer($from, $to, $amount) {
try {
$this->pdo->beginTransaction();
// get available amount of the transferer account
$sql = 'SELECT amount FROM accounts WHERE id=:from';
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute(array(":from" => $from));
$availableAmount = (int) $stmt->fetchColumn();
$stmt->closeCursor();
if ($availableAmount < $amount) {
echo 'Insufficient amount to transfer';
return false;
}
// deduct from the transferred account
$sql_update_from = 'UPDATE accounts
SET amount = amount - :amount
WHERE id = :from';
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql_update_from);
$stmt->execute(array(":from" => $from, ":amount" => $amount));
$stmt->closeCursor();
// add to the receiving account
$sql_update_to = 'UPDATE accounts
SET amount = amount + :amount
WHERE id = :to';
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql_update_to);
$stmt->execute(array(":to" => $to, ":amount" => $amount));
// commit the transaction
$this->pdo->commit();
echo 'The amount has been transferred successfully';
return true;
} catch (PDOException $e) {
$this->pdo->rollBack();
die($e->getMessage());
}
}
/*close the database connection*/
public function __destruct() {
// close the database connection
$this->pdo = null;
}
}
// test the transfer method
$obj = new TransactionDemo();
// transfer 30K from from account 1 to 2
$obj->transfer(1, 2, 30000);
// transfer 5K from from account 1 to 2
$obj->transfer(1, 2, 5000);
We
open a database connection in the __construct() method and close it in the __destruct() method. In the transfer() method:
First, we query amount of the transferred account and compare it with the transfer amount to check if the balance of the transferred account is sufficient.
Second, in case the amount is sufficient, we deduct the transfer amount from the transferred account and add it to the receiving account.
Third, we commit the transaction by calling the commit() method. If any error occurs, we call the rollBack() method in the catch block to rollback the transaction.
Let's test the transfer() method.
// transfer 30K from from account 1 to 2
$obj->transfer(1, 2, 30000);
We transferred 30K from John's account to Mary's. We got the following message:
Insufficient amount to transfer
Let's make another transfer:
// transfer 5K from from account 1 to 2
$obj->transfer(1, 2, 5000);
The script returns the following message:
The amount has been transferred successfully.
We have transferred money between two bank accounts successfully.
You can download the source code via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Transaction Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you step by step how to handle MySQL transactions in PHP to ensure data integrity.
PHP MySQL BLOB
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to handle BLOB data using PHP PDO. We will show you how to insert, update and select BLOB data in MySQL databases.
Sometimes, for the security reasons, you may need to store large data objects e.g., images, PDF files, and videos in the MySQL database.
MySQL provides a BLOB type that can hold a large amount of data. BLOB stands for the binary large data object. The maximum value of a BLOB object is specified by the available memory and the communication package size. You can change the communication package size by using the max_allowed_packet variable in MySQL and post_max_size in the PHP settings.
Let's see how PHP PDO handles the BLOB type in MySQL.
First, we
create a new table named files in the
sample database for practicing.
The files table contains three columns:
The id column is the
primary key,
auto-increment column.
The mime column stores the mime type of the file.
The data column whose data type is the BLOB that is used to store the content of the file.
The following
CREATE TABLE statement creates the files table:
CREATE TABLE files (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
mime VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
data BLOB NOT NULL
);
Second, we define a class called BlobDemo with the following code:
<?php
/**
* PHP MySQL BLOB Demo
*/
class BobDemo {
const DB_HOST = 'localhost';
const DB_NAME = 'classicmodels';
const DB_USER = 'root';
const DB_PASSWORD = '';
/*Open the database connection*/
public function __construct() {
// open database connection
$conStr = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s;charset=utf8", self::DB_HOST, self::DB_NAME);
try {
$this->pdo = new PDO($conStr, self::DB_USER, self::DB_PASSWORD);
//for prior PHP 5.3.6
//$conn->exec("set names utf8");
} catch (PDOException $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
}
/*close the database connection*/
public function __destruct() {
// close the database connection
$this->pdo = null;
}
}
In the __construct() method, we
open a database connection to the MySQL database, and in the __destruct() method, we close the connection.
Insert BLOB data into the database
PHP PDO provides a convenient way to work with BLOB data using the streams and prepare statements. To insert the content of a file into a BLOB column, you follow the steps below:
First, open the file for reading in binary mode.
Second, construct an
INSERT statement.
Third, bind the file handle to the prepared statement using the bindParam() method and call the execute() method to execute the query.
See the following insertBlob() method:
/*insert blob into the files table
* @param string $filePath
* @param string $mime mimetype
* @return bool*/
public function insertBlob($filePath, $mime) {
$blob = fopen($filePath, 'rb');
$sql = "INSERT INTO files(mime,data) VALUES(:mime,:data)";
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindParam(':mime', $mime);
$stmt->bindParam(':data', $blob, PDO::PARAM_LOB);
return $stmt->execute();
}
Notice that the PDO::PARAM_LOB instructs PDO to map the data as a stream.
Update an existing BLOB column
To update a BLOB column, you use the same technique as described in the inserting data into a BLOB column. See the following updateBlob() method:
/*update the files table with the new blob from the file specified
* by the filepath
* @param int $id
* @param string $filePath
* @param string $mime
* @return bool*/
function updateBlob($id, $filePath, $mime) {
$blob = fopen($filePath, 'rb');
$sql = "UPDATE files
SET mime = :mime,
data = :data
WHERE id = :id;";
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bindParam(':mime', $mime);
$stmt->bindParam(':data', $blob, PDO::PARAM_LOB);
$stmt->bindParam(':id', $id);
return $stmt->execute();
}
Query data from BLOB column
The following steps describe how to select data from a BLOB column:
First, construct a
SELECT statement.
Second, bind the corresponding parameter using the bindColumn() method of the PDOStatement object.
Third, execute the statement.
See the following selectBlob() method:
/*select data from the the files
* @param int $id
* @return array contains mime type and BLOB data*/
public function selectBlob($id) {
$sql = "SELECT mime,
data
FROM files
WHERE id = :id;";
$stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute(array(":id" => $id));
$stmt->bindColumn(1, $mime);
$stmt->bindColumn(2, $data, PDO::PARAM_LOB);
$stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_BOUND);
return array("mime" => $mime,
"data" => $data);
}
PHP MySQL BLOB examples
In the following examples, we will use the BlobDemo class to save a GIF image and a PDF file into the BLOB column of the files table.
PHP MySQL BLOB with image files
First, we insert binary data from the images/php-mysql-blob.gif file into the BLOB column of the files table as follows:
$blobObj = new BlobDemo();
// test insert gif image
$blobObj->insertBlob('images/php-mysql-blob.gif',"image/gif");
 Then, we can select the BLOB data and display it as a GIF image:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(1);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
Then, we can select the BLOB data and display it as a GIF image:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(1);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];

PHP MySQL BLOB with PDF files
The following code inserts the content of the pdf/php-mysql-blob.pdf PDF file into the BLOB column:
$blobObj = new BlobDemo();
// test insert pdf
$blobObj->insertBlob('pdf/php-mysql-blob.pdf',"application/pdf");
 Then, we can select the PDF data and render it in the web browser as follows:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(2);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
Then, we can select the PDF data and render it in the web browser as follows:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(2);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
 To replace the PDF file with the GIF image file, you use the
To replace the PDF file with the GIF image file, you use the updateBlob() method as follows:
$blobObj->updateBlob(2, 'images/php-mysql-blob.gif', "image/gif");
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(2);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
You can download the source code of this tutorial via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL BLOB Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to manage MySQL BLOB data including inserting, updating, and querying blob.
Was this tutorial helpful ?
Yes
No
MySQL Quick Start
What Is MySQL?
Install MySQL Database Server
Download MySQL Sample Database
Load Sample Database
 It works as expected. We've successfully connected to the MySQL server.
Let's try to change something in the code to make the script display an error message. If you set the
It works as expected. We've successfully connected to the MySQL server.
Let's try to change something in the code to make the script display an error message. If you set the  The error message shows that:
Access denied for user ''@'localhost' to database 'classicmodels'
because we don't have any blank user in the
The error message shows that:
Access denied for user ''@'localhost' to database 'classicmodels'
because we don't have any blank user in the 
 You can download the PHP script file via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Create Table Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you step by step how to use PDO object to create a table in the MySQL database.
Was this tutorial helpful ?
You can download the PHP script file via the following link:
Download PHP MySQL Create Table Source Code
In this tutorial, we have shown you step by step how to use PDO object to create a table in the MySQL database.
Was this tutorial helpful ?

 To insert data into a table, you follow the steps below:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
MySQL INSERT statement.
Call
To insert data into a table, you follow the steps below:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
MySQL INSERT statement.
Call 
 To
update data in a table, you use the following steps:
First,
connect to the MySQL database by creating a new PDO object.
Second, construct an
UPDATE statement to update data. If you want to pass values to the
To
update data in a table, you use the following steps:
First,
connect to the MySQL database by creating a new PDO object.
Second, construct an
UPDATE statement to update data. If you want to pass values to the  To delete data in a table, you use the following steps:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
DELETE statement to delete a row, multiple rows, or all rows in a table. If you want to delete all rows in a big table quickly and more efficiently, you use the
TRUNCATE TABLE statement.
Execute the
To delete data in a table, you use the following steps:
Connect to the MySQL database by creating a new instance of the PDO object.
Construct a
DELETE statement to delete a row, multiple rows, or all rows in a table. If you want to delete all rows in a big table quickly and more efficiently, you use the
TRUNCATE TABLE statement.
Execute the  A
transaction is a set of inter-dependent SQL statements that needs to execute in all-or-nothing mode. A transaction is successful if all SQL statements executed successfully. A failure of any statement will trigger the system to rollback to the original state to avoid data inconsistency.
A classic example of the transaction is a money transfer transaction from one bank account to another. It requires three steps:
Check the balance of the transferred account to see if the amount is sufficient for the transfer.
If the amount is sufficient, deduct the amount from the balance of the transferred account.
Add the transfer amount to the balance of the receiving account.
If an error occurs in the second step, the third step should not continue. In addition, if an error occurs in the third step, the second step must be reversed. The amounts of both bank accounts are intact in case of failure or adjusted correctly if the transaction is completed successfully.
A
transaction is a set of inter-dependent SQL statements that needs to execute in all-or-nothing mode. A transaction is successful if all SQL statements executed successfully. A failure of any statement will trigger the system to rollback to the original state to avoid data inconsistency.
A classic example of the transaction is a money transfer transaction from one bank account to another. It requires three steps:
Check the balance of the transferred account to see if the amount is sufficient for the transfer.
If the amount is sufficient, deduct the amount from the balance of the transferred account.
Add the transfer amount to the balance of the receiving account.
If an error occurs in the second step, the third step should not continue. In addition, if an error occurs in the third step, the second step must be reversed. The amounts of both bank accounts are intact in case of failure or adjusted correctly if the transaction is completed successfully.
 Let's take a look at the following
Let's take a look at the following  Then, we can select the BLOB data and display it as a GIF image:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(1);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
Then, we can select the BLOB data and display it as a GIF image:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(1);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
 Then, we can select the PDF data and render it in the web browser as follows:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(2);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];
Then, we can select the PDF data and render it in the web browser as follows:
$a = $blobObj->selectBlob(2);
header("Content-Type:" . $a['mime']);
echo $a['data'];