PHP MySQL
PHP MySQL Database
- Database Queries
A query is a question or a request.
We can query a database for specific information and have a recordset returned.
- Facts About MySQL Database
MySQL is the de-facto standard database system for web sites with HUGE volumes of both data and end-users (like Facebook, Twitter, and Wikipedia).
Another great thing about MySQL is that it can be scaled down to support embedded database applications.
PHP Connect to MySQL
PHP 5 and later can work with a MySQL database using:
MySQLi extension (the "i" stands for improved)
PDO (PHP Data Objects)
Earlier versions of PHP used the MySQL extension.
However, this extension was deprecated in 2012.
- Should I Use MySQLi or PDO?
If you need a short answer, it would be "Whatever you like".
Both MySQLi and PDO have their advantages:
PDO will work on 12 different database systems, whereas MySQLi will only work with MySQL databases.
So, if you have to switch your project to use another database, PDO makes the process easy.
You only have to change the connection string and a few queries.
With MySQLi, you will need to rewrite the entire code - queries included.
Both are object-oriented, but MySQLi also offers a procedural API.
Both support Prepared Statements.
Prepared Statements protect from SQL injection, and are very important for web application security.
- MySQL Examples in Both MySQLi and PDO Syntax
In this, and in the following chapters we demonstrate three ways of working with PHP and MySQL:
MySQLi (object-oriented)
MySQLi (procedural)
PDO
- Open a Connection to MySQL
Before we can access data in the MySQL database, we need to be able to connect to the server:
Example (MySQLi Object-Oriented)
Object-Oriented usese the -> symbol!
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
echo "Connected successfully";
?>
Note on the object-oriented example above: $connect_error was broken until PHP 5.2.9 and 5.3.0.
If you need to ensure compatibility with PHP versions prior to 5.2.9 and 5.3.0, use the following code instead:
// Check connection
if (mysqli_connect_error()) {
die("Database connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
echo "Connected successfully";
?>
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=myDB", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
echo "Connected successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo "Connection failed: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
Note: In the PDO example above we have also specified a database (myDB).
PDO require a valid database to connect to.
If no database is specified, an exception is thrown.
Tip: A great benefit of PDO is that it has an exception class to handle any problems that may occur in our database queries.
If an exception is thrown within the try{ } block, the script stops executing and flows directly to the first catch(){ } block.
- Close the Connection
The connection will be closed automatically when the script ends.
To close the connection before, use the following:
MySQLi Object-Oriented:
$conn->close();
MySQLi Procedural:
mysqli_close($conn);
PDO:
$conn = null;
PHP Create a MySQL Database
A database consists of one or more tables.
You will need special CREATE privileges to create or to delete a MySQL database.
- Create a MySQL Database Using MySQLi and PDO
The CREATE DATABASE statement is used to create a database in MySQL.
The following examples create a database named "myDB":
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// Create database
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE myDB";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Database created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error creating database: " . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Note: When you create a new database, you must only specify the first three arguments to the mysqli object (servername, username and password).
Tip: If you have to use a specific port,
add an empty string for the database-name argument, like this: new mysqli("localhost", "root", "asdf1234", ", port)
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
// Create database
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE myDB";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "Database created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error creating database: " . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Note: The following PDO example create a database named "myDBPDO":
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE myDBPDO";
// use exec() because no results are returned
$conn->exec($sql);
echo "Database created successfully<br>";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
Tip: A great benefit of PDO is that it has exception class to handle any problems that may occur in our database queries.
If an exception is thrown within the try{ } block, the script stops executing and flows directly to the first catch(){ } block.
In the catch block above we echo the SQL statement and the generated error message.
PHP MySQL Create Table
A database table has its own unique name and consists of columns and rows.
- Create a MySQL Table Using MySQLi and PDO
The CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a table in MySQL.
We will create a table named "MyGuests", with five columns: "id", "firstname", "lastname", "email" and "reg_date":
CREATE TABLE MyGuests (
id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
firstname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50),
reg_date TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
Notes on the table above:
The data type specifies what type of data the column can hold.
For a complete reference of all the available data types, go to our
Data Types reference.
After the data type, you can specify other optional attributes for each column:
NOT NULL - Each row must contain a value for that column, null values are not allowed
DEFAULT value - Set a default value that is added when no other value is passed
UNSIGNED - Used for number types, limits the stored data to positive numbers and zero
AUTO INCREMENT - MySQL automatically increases the value of the field by 1 each time a new record is added
PRIMARY KEY - Used to uniquely identify the rows in a table.
The column with PRIMARY KEY setting is often an ID number, and is often used with AUTO_INCREMENT
Each table should have a primary key column (in this case: the "id" column).
Its value must be unique for each record in the table.
The following examples shows how to create the table in PHP:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// sql to create table
$sql = "CREATE TABLE MyGuests (
id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, firstname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50),
reg_date TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Table MyGuests created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error creating table: " . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
// sql to create table
$sql = "CREATE TABLE MyGuests (
id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, firstname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50),
reg_date TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "Table MyGuests created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error creating table: " . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
// sql to create table
$sql = "CREATE TABLE MyGuests (
id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, firstname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50),
reg_date TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)";
// use exec() because no results are returned
$conn->exec($sql);
echo "Table MyGuests created successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
PHP MySQL Insert Data
- Insert Data Into MySQL Using MySQLi and PDO
After a database and a table have been created, we can start adding data in them.
Here are some syntax rules to follow:
The SQL query must be quoted in PHP
String values inside the SQL query must be quoted
Numeric values must not be quoted
The word NULL must not be quoted
The INSERT INTO statement is used to add new records to a MySQL table:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3,...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...)
In the previous chapter we created an empty table named "MyGuests" with five columns: "id", "firstname", "lastname", "email" and "reg_date".
Now, let us fill the table with data.
Note: If a column is AUTO_INCREMENT (like the "id" column) or TIMESTAMP with default update of current_timesamp (like the "reg_date" column), it is no need to be specified in the SQL query; MySQL will automatically add the value.
The following examples add a new record to the "MyGuests" table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "New record created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "New record created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')";
// use exec() because no results are returned
$conn->exec($sql);
echo "New record created successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
PHP MySQL Get Last Inserted ID
- Get ID of The Last Inserted Record
If we perform an INSERT or UPDATE on a table with an AUTO_INCREMENT field, we can get the ID of the last inserted/updated record immediately.
In the table "MyGuests", the "id" column is an AUTO_INCREMENT field:
CREATE TABLE MyGuests (
id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
firstname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50),
reg_date TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
The following examples are equal to the examples from the previous page (PHP Insert Data Into MySQL), except that we have added one single line of code to retrieve the ID of the last inserted record.
We also echo the last inserted ID:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
$last_id = $conn->insert_id;
echo "New record created successfully.
Last inserted ID is: " . $last_id;
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
$last_id = mysqli_insert_id($conn);
echo "New record created successfully.
Last inserted ID is: " . $last_id;
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')";
// use exec() because no results are returned
$conn->exec($sql);
$last_id = $conn->lastInsertId();
echo "New record created successfully.
Last inserted ID is: " . $last_id;
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
PHP MySQL Insert Multiple Records
- Insert Multiple Records Into MySQL Using MySQLi and PDO
Multiple SQL statements must be executed with the mysqli_multi_query() function.
The following examples add three new records to the "MyGuests" table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com');";
$sql .= "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('Mary', 'Moe', 'mary@example.com');";
$sql .= "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('Julie', 'Dooley', 'julie@example.com')";
if ($conn->multi_query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "New records created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Note that each SQL statement must be separated by a semicolon.
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com');";
$sql .= "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('Mary', 'Moe', 'mary@example.com');";
$sql .= "INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES ('Julie', 'Dooley', 'julie@example.com')";
if (mysqli_multi_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "New records created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
The PDO way is a little bit different:
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
// begin the transaction
$conn->beginTransaction();
// our SQL statements
$conn->exec("INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john@example.com')");
$conn->exec("INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES ('Mary', 'Moe', 'mary@example.com')");
$conn->exec("INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES ('Julie', 'Dooley', 'julie@example.com')");
// commit the transaction
$conn->commit();
echo "New records created successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
// roll back the transaction if something failed
$conn->rollback();
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
PHP MySQL Prepared Statements
Prepared statements are very useful against SQL injections.
- Prepared Statements and Bound Parameters
A prepared statement is a feature used to execute the same (or similar) SQL statements repeatedly with high efficiency.
Prepared statements basically work like this:
Prepare: An SQL statement template is created and sent to the database.
Certain values are left unspecified, called parameters (labeled "?").
Example: INSERT INTO MyGuests VALUES(?, ?, ?)
The database parses, compiles, and performs query optimization on the SQL statement template, and stores the result without executing it
Execute: At a later time, the application binds the values to the parameters, and the database executes the statement.
The application may execute the statement as many times as it wants with different values
Compared to executing SQL statements directly, prepared statements have three main advantages:
Prepared statements reduce parsing time as the preparation on the query is done only once (although the statement is executed multiple times)
Bound parameters minimize bandwidth to the server as you need send only the parameters each time, and not the whole query
Prepared statements are very useful against SQL injections, because parameter values, which are transmitted later using a different protocol, need not be correctly escaped.
If the original statement template is not derived from external input, SQL injection cannot occur.
- Prepared Statements in MySQLi
The following example uses prepared statements and bound parameters in MySQLi:
Example (MySQLi with Prepared Statements)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// prepare and bind
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES (?, ?, ?)");
$stmt->bind_param("sss", $firstname, $lastname, $email);
// set parameters and execute
$firstname = "John";
$lastname = "Doe";
$email = "john@example.com";
$stmt->execute();
$firstname = "Mary";
$lastname = "Moe";
$email = "mary@example.com";
$stmt->execute();
$firstname = "Julie";
$lastname = "Dooley";
$email = "julie@example.com";
$stmt->execute();
echo "New records created successfully";
$stmt->close();
$conn->close();
?>
Code lines to explain from the example above:
"INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES (?, ?, ?)"
In our SQL, we insert a question mark (?) where we want to substitute in an integer, string, double or blob value.
Then, have a look at the bind_param() function:
$stmt->bind_param("sss", $firstname, $lastname, $email);
This function binds the parameters to the SQL query and tells the database what the parameters are.
The "sss" argument lists the types of data that the parameters are.
The s character tells mysql that the parameter is a string.
The argument may be one of four types:
i - integer
d - double
s - string
b - BLOB
We must have one of these for each parameter.
By telling mysql what type of data to expect, we minimize the risk of SQL injections.
Note: If we want to insert any data from external sources (like user input), it is very important that the data is sanitized and validated.
- Prepared Statements in PDO
The following example uses prepared statements and bound parameters in PDO:
Example (PDO with Prepared Statements)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
// prepare sql and bind parameters
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email)
VALUES (:firstname, :lastname, :email)");
$stmt->bindParam(':firstname', $firstname);
$stmt->bindParam(':lastname', $lastname);
$stmt->bindParam(':email', $email);
// insert a row
$firstname = "John";
$lastname = "Doe";
$email = "john@example.com";
$stmt->execute();
// insert another row
$firstname = "Mary";
$lastname = "Moe";
$email = "mary@example.com";
$stmt->execute();
// insert another row
$firstname = "Julie";
$lastname = "Dooley";
$email = "julie@example.com";
$stmt->execute();
echo "New records created successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
PHP MySQL Select Data
- Select Data From a MySQL Database
The SELECT statement is used to select data from one or more tables:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
or we can use the * character to select ALL columns from a table:
SELECT *
FROM table_name
To learn more about SQL, please visit our SQL tutorial.
- Select Data With MySQLi
The following example selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table and displays it on the page:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Run example »
Code lines to explain from the example above:
First, we set up an SQL query that selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table.
The next line of code runs the query and puts the resulting data into a variable called $result.
Then, the function num_rows() checks if there are more than zero rows returned.
If there are more than zero rows returned, the function fetch_assoc() puts all the results into an associative array that we can loop through.
The while() loop loops through the result set and outputs the data from the id, firstname and lastname columns.
The following example shows the same as the example above, in the MySQLi procedural way:
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Run example »
You can also put the result in an HTML table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
echo "<table><tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th></tr>";
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "<tr><td>".$row["id"]."</td><td>".$row["firstname"]." ".$row["lastname"]."</td></tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Run example »
- Select Data With PDO (+ Prepared Statements)
The following example uses prepared statements.
It selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table and displays it in an HTML table:
Example (PDO)
<?php
echo "<table style='border: solid 1px black;'>";
echo "<tr><th>Id</th><th>Firstname</th><th>Lastname</th></tr>";
class TableRows extends RecursiveIteratorIterator {
function __construct($it) { parent::__construct($it, self::LEAVES_ONLY); }
function current() {
return "<td style='width:150px;border:1px solid black;'>" . parent::current(). "</td>";
}
function beginChildren() { echo "<tr>"; }
function endChildren() { echo "</tr>" . "\n";
} }
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests"); $stmt->execute();
// set the resulting array to associative
$result = $stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC); foreach(new TableRows(new RecursiveArrayIterator($stmt->fetchAll())) as $k=>$v) { echo $v;
}
}
catch(PDOException $e) {
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
echo "</table>";
?>
Run example »
PHP MySQL Use The WHERE Clause
- Select and Filter Data From a MySQL Database
The WHERE clause is used to filter records.
The WHERE clause is used to extract only those records that fulfill a specified condition.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name WHERE column_name operator value
To learn more about SQL, please visit our SQL tutorial.
- Select and Filter Data With MySQLi
The following example selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table where the lastname is "Doe", and displays it on the page:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests WHERE lastname='Doe'";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Run example »
Code lines to explain from the example above:
First, we set up the SQL query that selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table where the lastname is "Doe".
The next line of code runs the query and puts the resulting data into a variable called $result.
Then, the function num_rows() checks if there are more than zero rows returned.
If there are more than zero rows returned, the function fetch_assoc() puts all the results into an associative array that we can loop through.
The while() loop loops through the result set and outputs the data from the id, firstname and lastname columns.
The following example shows the same as the example above, in the MySQLi procedural way:
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests WHERE lastname='Doe'";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Run example »
You can also put the result in an HTML table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests WHERE lastname='Doe'";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
echo "<table><tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th></tr>";
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "<tr><td>".$row["id"]."</td><td>".$row["firstname"]." ".$row["lastname"]."</td></tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Run example »
- Select Data With PDO (+ Prepared Statements)
The following example uses prepared statements.
It selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table where the lastname is "Doe", and displays it in an HTML table:
Example (PDO)
<?php
echo "<table style='border: solid 1px black;'>";
echo "<tr><th>Id</th><th>Firstname</th><th>Lastname</th></tr>";
class TableRows extends RecursiveIteratorIterator {
function __construct($it) { parent::__construct($it, self::LEAVES_ONLY); }
function current() {
return "<td style='width:150px;border:1px solid black;'>" . parent::current(). "</td>";
}
function beginChildren() { echo "<tr>"; }
function endChildren() { echo "</tr>" . "\n";
} }
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests WHERE lastname='Doe'"); $stmt->execute();
// set the resulting array to associative
$result = $stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC); foreach(new TableRows(new RecursiveArrayIterator($stmt->fetchAll())) as $k=>$v) { echo $v;
}
}
catch(PDOException $e) {
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
echo "</table>";
?>
Run example »
PHP MySQL Use The ORDER BY Clause
- Select and Order Data From a MySQL Database
The ORDER BY clause is used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending order.
The ORDER BY clause sorts the records in ascending order by default.
To sort the records in descending order, use the DESC keyword.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name(s) ASC|DESC
To learn more about SQL, please visit our SQL tutorial.
- Select and Order Data With MySQLi
The following example selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table.
The records will be ordered by the lastname column:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests ORDER BY lastname";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Run example »
Code lines to explain from the example above:
First, we set up the SQL query that selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table.
The records will be ordered by the lastname column.
The next line of code runs the query and puts the resulting data into a variable called $result.
Then, the function num_rows() checks if there are more than zero rows returned.
If there are more than zero rows returned, the function fetch_assoc() puts all the results into an associative array that we can loop through.
The while() loop loops through the result set and outputs the data from the id, firstname and lastname columns.
The following example shows the same as the example above, in the MySQLi procedural way:
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests ORDER BY lastname";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Run example »
You can also put the result in an HTML table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests ORDER BY lastname";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
echo "<table><tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th></tr>";
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "<tr><td>".$row["id"]."</td><td>".$row["firstname"]." ".$row["lastname"]."</td></tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Run example »
- Select Data With PDO (+ Prepared Statements)
The following example uses prepared statements.
Here we select the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table.
The records will be ordered by the lastname column, and it will be displayed in an HTML table:
Example (PDO)
<?php
echo "<table style='border: solid 1px black;'>";
echo "<tr><th>Id</th><th>Firstname</th><th>Lastname</th></tr>";
class TableRows extends RecursiveIteratorIterator {
function __construct($it) { parent::__construct($it, self::LEAVES_ONLY); }
function current() {
return "<td style='width:150px;border:1px solid black;'>" . parent::current(). "</td>";
}
function beginChildren() { echo "<tr>"; }
function endChildren() { echo "</tr>" . "\n";
} }
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests ORDER BY lastname"); $stmt->execute();
// set the resulting array to associative
$result = $stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC); foreach(new TableRows(new RecursiveArrayIterator($stmt->fetchAll())) as $k=>$v) { echo $v;
}
}
catch(PDOException $e) {
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
echo "</table>";
?>
Run example »
PHP MySQL Delete Data
- Delete Data From a MySQL Table Using MySQLi and PDO
The DELETE statement is used to delete records from a table:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE some_column = some_value
Notice the WHERE clause in the DELETE syntax: The WHERE clause specifies which record or records that should be deleted.
If you omit the WHERE clause, all records will be deleted!
To learn more about SQL, please visit our SQL tutorial.
Let's look at the "MyGuests" table:
| id |
firstname |
lastname |
email |
reg_date |
| 1 |
John |
Doe |
john@example.com |
2014-10-22 14:26:15 |
| 2 |
Mary |
Moe |
mary@example.com |
2014-10-23 10:22:30 |
| 3 |
Julie |
Dooley |
julie@example.com |
2014-10-26 10:48:23 |
The following examples delete the record with id=3 in the "MyGuests" table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// sql to delete a record
$sql = "DELETE FROM MyGuests WHERE id=3";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Record deleted successfully";
} else {
echo "Error deleting record: " . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
// sql to delete a record
$sql = "DELETE FROM MyGuests WHERE id=3";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "Record deleted successfully";
} else {
echo "Error deleting record: " . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
// sql to delete a record
$sql = "DELETE FROM MyGuests WHERE id=3";
// use exec() because no results are returned
$conn->exec($sql);
echo "Record deleted successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
After the record is deleted, the table will look like this:
| id |
firstname |
lastname |
email |
reg_date |
| 1 |
John |
Doe |
john@example.com |
2014-10-22 14:26:15 |
| 2 |
Mary |
Moe |
mary@example.com |
2014-10-23 10:22:30 |
PHP MySQL Update Data
- Update Data In a MySQL Table Using MySQLi and PDO
The UPDATE statement is used to update existing records in a table:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1=value, column2=value2,...
WHERE some_column=some_value
Notice the WHERE clause in the UPDATE syntax: The WHERE clause specifies which record or records that should be updated.
If you omit the WHERE clause, all records will be updated!
To learn more about SQL, please visit our SQL tutorial.
Let's look at the "MyGuests" table:
| id |
firstname |
lastname |
email |
reg_date |
| 1 |
John |
Doe |
john@example.com |
2014-10-22 14:26:15 |
| 2 |
Mary |
Moe |
mary@example.com |
2014-10-23 10:22:30 |
The following examples update the record with id=2 in the "MyGuests" table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "UPDATE MyGuests SET lastname='Doe' WHERE id=2";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Record updated successfully";
} else {
echo "Error updating record: " . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "UPDATE MyGuests SET lastname='Doe' WHERE id=2";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "Record updated successfully";
} else {
echo "Error updating record: " . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "asdf1234";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "UPDATE MyGuests SET lastname='Doe' WHERE id=2";
// Prepare statement
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
// execute the query
$stmt->execute();
// echo a message to say the UPDATE succeeded
echo $stmt->rowCount() . " records UPDATED successfully";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
After the record is updated, the table will look like this:
| id |
firstname |
lastname |
email |
reg_date |
| 1 |
John |
Doe |
john@example.com |
2014-10-22 14:26:15 |
| 2 |
Mary |
Doe |
mary@example.com |
2014-10-23 10:22:30 |
PHP MySQL Limit Data Selections
- Limit Data Selections From a MySQL Database
MySQL provides a LIMIT clause that is used to specify the number of records to return.
The LIMIT clause makes it easy to code multi page results or pagination with SQL, and is very useful on large tables.
Returning a large number of records can impact on performance.
Assume we wish to select all records from 1 - 30 (inclusive) from a table called "Orders".
The SQL query would then look like this:
$sql = "SELECT * FROM Orders LIMIT 30";
When the SQL query above is run, it will return the first 30 records.
What if we want to select records 16 - 25 (inclusive)?
Mysql also provides a way to handle this: by using OFFSET.
The SQL query below says "return only 10 records, start on record 16 (OFFSET 15)":
$sql = "SELECT * FROM Orders LIMIT 10 OFFSET 15";
You could also use a shorter syntax to achieve the same result:
$sql = "SELECT * FROM Orders LIMIT 15, 10";
Notice that the numbers are reversed when you use a comma.
Select Data With MySQLi
The following example selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table and displays it on the page:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
The following example shows the same as the example above, in the MySQLi procedural way:
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
You can also put the result in an HTML table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
echo "<table><tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th></tr>";
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "<tr><td>".$row["id"]."</td><td>".$row["firstname"]." ".$row["lastname"]."</td></tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Select Data With PDO (+ Prepared Statements)
The following example uses prepared statements.
It selects the id, firstname and lastname columns from the MyGuests table and
displays it in an HTML table:
Example (PDO)
<?php
echo "<table style='border: solid 1px black;'>";
echo "<tr><th>Id</th><th>Firstname</th><th>Lastname</th></tr>";
class TableRows extends RecursiveIteratorIterator {
function __construct($it) {
parent::__construct($it, self::LEAVES_ONLY);
}
function current() {
return "<td style='width:150px;border:1px solid black;'>" . parent::current(). "</td>";
}
function beginChildren() {
echo "<tr>";
}
function endChildren() {
echo "</tr>" . "\n";
}
}
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests");
$stmt->execute();
// set the resulting array to associative
$result = $stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
foreach(new TableRows(new RecursiveArrayIterator($stmt->fetchAll())) as $k=>$v) {
echo $v;
}
} catch(PDOException $e) {
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
echo "</table>";
?>
Create a MySQL Database Using MySQLi and PDO
The CREATE DATABASE statement is used to create a database in MySQL.
The following examples create a database named "myDB":
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// Create database
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE myDB";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Database created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error creating database: " . $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Note: When you create a new database, you must only specify the first three arguments to the mysqli object (servername, username and password).
Tip: If you have to use a specific port,
add an empty string for the database-name argument, like this: new mysqli("localhost", "username", "password", ", port)
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
// Create database
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE myDB";
if (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) {
echo "Database created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error creating database: " . mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Note: The following PDO example create a database named "myDBPDO":
Example (PDO)
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
try {
$conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE myDBPDO";
// use exec() because no results are returned
$conn->exec($sql);
echo "Database created successfully<br>";
} catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo $sql . "<br>" . $e->getMessage();
}
$conn = null;
?>
Tip: A great benefit of PDO is that it has exception class to handle any problems that may
occur in our database queries. If an exception is thrown within the try{ } block, the script stops executing and flows directly to the first catch(){ } block. In the catch block above we echo the SQL statement and the generated error message.
PHP MySQL CRUD Application
In this tutorial you'll learn how to build a CRUD application with PHP and MySQL.
What is CRUD
CRUD is an acronym for Create, Read, Update, and Delete. CRUD operations are basic data manipulation for database. We've already learned how to perform create (i.e. insert), read (i.e. select), update and delete operations in previous chapters. In this tutorial we'll create a simple PHP application to perform all these operations on a MySQL database table at one place.
Well, let's start by Create table which we'll use in all of our example.
Create Database Table
Execute the following SQL query to create a table named employees inside your MySQL database. We will use this table for all of our future operations.
Example
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
address VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
salary INT(10) NOT NULL
);
Create Config File
After Create table, we need create a PHP script in order to connect to the MySQL database server. Let's create a file named "config.php" and put the following code inside it.
We'll later include this config file in other pages using the PHP require_once() function.
Example
<?php
/* Database credentials. Assuming you are running MySQL
server with default setting (user 'root' with no password) */
define('DB_SERVER', 'localhost');
define('DB_USERNAME', 'root');
define('DB_PASSWORD', '');
define('DB_NAME', 'demo');
/* Attempt to connect to MySQL database */
$link = mysqli_connect(DB_SERVER, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD, DB_NAME);
// Check connection
if($link === false){
die("ERROR: Could not connect. " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
?>
<?php
/* Database credentials. Assuming you are running MySQL
server with default setting (user 'root' with no password) */
define('DB_SERVER', 'localhost');
define('DB_USERNAME', 'root');
define('DB_PASSWORD', '');
define('DB_NAME', 'demo');
/* Attempt to connect to MySQL database */
$mysqli = new mysqli(DB_SERVER, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD, DB_NAME);
// Check connection
if($mysqli === false){
die("ERROR: Could not connect. " . $mysqli->connect_error);
}
?>
<?php
/* Database credentials. Assuming you are running MySQL
server with default setting (user 'root' with no password) */
define('DB_SERVER', 'localhost');
define('DB_USERNAME', 'root');
define('DB_PASSWORD', '');
define('DB_NAME', 'demo');
/* Attempt to connect to MySQL database */
try{
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=" . DB_SERVER . ";dbname=" . DB_NAME, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD);
// Set the PDO error mode to exception
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
} catch(PDOException $e){
die("ERROR: Could not connect. " . $e->getMessage());
}
?>
If you've downloaded the Object Oriented or PDO code examples using the download button, please remove the text "-oo-format" or "-pdo-format" from file names before testing the code.
Note: Replace the credentials according to your MySQL server setting before testing this code, for example, replace the database name 'demo' with your own database name, replace username 'root' with your own database username, specify database password if there's any.
Create Landing Page
First we will create a landing page for our CRUD application that contains a data grid showing the records from the employees database table. It also has action icons for each record displayed in the grid, that you may choose to view its details, update it, or delete it.
We'll also add a create button on the top of the data grid that can be used for creating new records in the employees table. Create a file named "index.php" and put the following code in it:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Dashboard</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/font-awesome/4.7.0/css/font-awesome.min.css">
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/popper.js@1.16.1/dist/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
table tr td:last-child{
width: 120px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$('[data-toggle="tooltip"]').tooltip();
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="mt-5 mb-3 clearfix">
<h2 class="pull-left">Employees Details</h3>
<a href="create.php" class="btn btn-success pull-right"><i class="fa fa-plus"></i> Add New Employee</a>
</div>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Attempt select query execution
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees";
if($result = mysqli_query($link, $sql)){
if(mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0){
echo '<table class="table table-bordered table-striped">';
echo "<thead>";
echo "<tr>";
echo "<th>#</th>";
echo "<th>Name</th>";
echo "<th>Address</th>";
echo "<th>Salary</th>";
echo "<th>Action</th>";
echo "</tr>";
echo "</thead>";
echo "<tbody>";
while($row = mysqli_fetch_array($result)){
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>" . $row['id'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['name'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['address'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['salary'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>";
echo '<a href="read.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" class="mr-3" title="View Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-eye"></span></a>';
echo '<a href="update.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" class="mr-3" title="Update Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-pencil"></span></a>';
echo '<a href="delete.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" title="Delete Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-trash"></span></a>';
echo "</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "</tbody>";
echo "</table>";
// Free result set
mysqli_free_result($result);
} else{
echo '<div class="alert alert-danger"><em>No records were found.</em></div>';
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
// Close connection
mysqli_close($link);
?>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Dashboard</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/font-awesome/4.7.0/css/font-awesome.min.css">
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/popper.js@1.16.1/dist/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
table tr td:last-child{
width: 120px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$('[data-toggle="tooltip"]').tooltip();
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="mt-5 mb-3 clearfix">
<h2 class="pull-left">Employees Details</h3>
<a href="create.php" class="btn btn-success pull-right"><i class="fa fa-plus"></i> Add New Employee</a>
</div>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Attempt select query execution
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees";
if($result = $mysqli->query($sql)){
if($result->num_rows > 0){
echo '<table class="table table-bordered table-striped">';
echo "<thead>";
echo "<tr>";
echo "<th>#</th>";
echo "<th>Name</th>";
echo "<th>Address</th>";
echo "<th>Salary</th>";
echo "<th>Action</th>";
echo "</tr>";
echo "</thead>";
echo "<tbody>";
while($row = $result->fetch_array()){
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>" . $row['id'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['name'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['address'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['salary'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>";
echo '<a href="read.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" class="mr-3" title="View Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-eye"></span></a>';
echo '<a href="update.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" class="mr-3" title="Update Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-pencil"></span></a>';
echo '<a href="delete.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" title="Delete Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-trash"></span></a>';
echo "</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "</tbody>";
echo "</table>";
// Free result set
$result->free();
} else{
echo '<div class="alert alert-danger"><em>No records were found.</em></div>';
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
// Close connection
$mysqli->close();
?>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Dashboard</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/font-awesome/4.7.0/css/font-awesome.min.css">
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/popper.js@1.16.1/dist/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
table tr td:last-child{
width: 120px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$('[data-toggle="tooltip"]').tooltip();
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="mt-5 mb-3 clearfix">
<h2 class="pull-left">Employees Details</h3>
<a href="create.php" class="btn btn-success pull-right"><i class="fa fa-plus"></i> Add New Employee</a>
</div>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Attempt select query execution
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees";
if($result = $pdo->query($sql)){
if($result->rowCount() > 0){
echo '<table class="table table-bordered table-striped">';
echo "<thead>";
echo "<tr>";
echo "<th>#</th>";
echo "<th>Name</th>";
echo "<th>Address</th>";
echo "<th>Salary</th>";
echo "<th>Action</th>";
echo "</tr>";
echo "</thead>";
echo "<tbody>";
while($row = $result->fetch()){
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>" . $row['id'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['name'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['address'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['salary'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>";
echo '<a href="read.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" class="mr-3" title="View Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-eye"></span></a>';
echo '<a href="update.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" class="mr-3" title="Update Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-pencil"></span></a>';
echo '<a href="delete.php?id='. $row['id'] .'" title="Delete Record" data-toggle="tooltip"><span class="fa fa-trash"></span></a>';
echo "</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "</tbody>";
echo "</table>";
// Free result set
unset($result);
} else{
echo '<div class="alert alert-danger"><em>No records were found.</em></div>';
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
// Close connection
unset($pdo);
?>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Once employees table is populated with some records the landing page i.e. the CRUD data grid may look something like the picture shown below:
Tip: We've used the Bootstrap framework to make this CRUD application layout quickly and beautifully. Bootstrap is the most popular and powerful front-end framework for faster and easier responsive web development. Please, checkout the Bootstrap tutorial section to learn more about this framework.
Create Create Page
In this section we'll build the Create functionality of our CRUD application.
Let's create a file named "create.php" and put the following code inside it. It will generate a web form that can be used to insert records in the employees table.
Example
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Define variables and initialize with empty values
$name = $address = $salary = "";
$name_err = $address_err = $salary_err = "";
// Processing form data when form is submitted
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST"){
// Validate name
$input_name = trim($_POST["name"]);
if(empty($input_name)){
$name_err = "Please enter a name.";
} elseif(!filter_var($input_name, FILTER_VALIDATE_REGEXP, array("options"=>array("regexp"=>"/^[a-zA-Z\s]+$/")))){
$name_err = "Please enter a valid name.";
} else{
$name = $input_name;
}
// Validate address
$input_address = trim($_POST["address"]);
if(empty($input_address)){
$address_err = "Please enter an address.";
} else{
$address = $input_address;
}
// Validate salary
$input_salary = trim($_POST["salary"]);
if(empty($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter the salary amount.";
} elseif(!ctype_digit($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter a positive integer value.";
} else{
$salary = $input_salary;
}
// Check input errors before inserting in database
if(empty($name_err) && empty($address_err) && empty($salary_err)){
// Prepare an insert statement
$sql = "INSERT INTO employees (name, address, salary) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
if($stmt = mysqli_prepare($link, $sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt, "sss", $param_name, $param_address, $param_salary);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_address = $address;
$param_salary = $salary;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if(mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)){
// Records created successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
mysqli_stmt_close($stmt);
}
// Close connection
mysqli_close($link);
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Create Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5">Create Record</h3>
<p>Please fill this form and submit to add employee record to the database.</p>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]); ?>" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($name_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $name_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<textarea name="address" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($address_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>"><?php echo $address; ?></textarea>
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $address_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($salary_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $salary; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $salary_err;?></span>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Submit">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Define variables and initialize with empty values
$name = $address = $salary = "";
$name_err = $address_err = $salary_err = "";
// Processing form data when form is submitted
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST"){
// Validate name
$input_name = trim($_POST["name"]);
if(empty($input_name)){
$name_err = "Please enter a name.";
} elseif(!filter_var($input_name, FILTER_VALIDATE_REGEXP, array("options"=>array("regexp"=>"/^[a-zA-Z\s]+$/")))){
$name_err = "Please enter a valid name.";
} else{
$name = $input_name;
}
// Validate address
$input_address = trim($_POST["address"]);
if(empty($input_address)){
$address_err = "Please enter an address.";
} else{
$address = $input_address;
}
// Validate salary
$input_salary = trim($_POST["salary"]);
if(empty($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter the salary amount.";
} elseif(!ctype_digit($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter a positive integer value.";
} else{
$salary = $input_salary;
}
// Check input errors before inserting in database
if(empty($name_err) && empty($address_err) && empty($salary_err)){
// Prepare an insert statement
$sql = "INSERT INTO employees (name, address, salary) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
if($stmt = $mysqli->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bind_param("sss", $param_name, $param_address, $param_salary);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_address = $address;
$param_salary = $salary;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
// Records created successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
$stmt->close();
}
// Close connection
$mysqli->close();
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Create Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5">Create Record</h3>
<p>Please fill this form and submit to add employee record to the database.</p>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]); ?>" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($name_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $name_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<textarea name="address" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($address_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>"><?php echo $address; ?></textarea>
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $address_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($salary_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $salary; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $salary_err;?></span>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Submit">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Define variables and initialize with empty values
$name = $address = $salary = "";
$name_err = $address_err = $salary_err = "";
// Processing form data when form is submitted
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST"){
// Validate name
$input_name = trim($_POST["name"]);
if(empty($input_name)){
$name_err = "Please enter a name.";
} elseif(!filter_var($input_name, FILTER_VALIDATE_REGEXP, array("options"=>array("regexp"=>"/^[a-zA-Z\s]+$/")))){
$name_err = "Please enter a valid name.";
} else{
$name = $input_name;
}
// Validate address
$input_address = trim($_POST["address"]);
if(empty($input_address)){
$address_err = "Please enter an address.";
} else{
$address = $input_address;
}
// Validate salary
$input_salary = trim($_POST["salary"]);
if(empty($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter the salary amount.";
} elseif(!ctype_digit($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter a positive integer value.";
} else{
$salary = $input_salary;
}
// Check input errors before inserting in database
if(empty($name_err) && empty($address_err) && empty($salary_err)){
// Prepare an insert statement
$sql = "INSERT INTO employees (name, address, salary) VALUES (:name, :address, :salary)";
if($stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bindParam(":name", $param_name);
$stmt->bindParam(":address", $param_address);
$stmt->bindParam(":salary", $param_salary);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_address = $address;
$param_salary = $salary;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
// Records created successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
unset($stmt);
}
// Close connection
unset($pdo);
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Create Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5">Create Record</h3>
<p>Please fill this form and submit to add employee record to the database.</p>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]); ?>" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($name_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $name_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<textarea name="address" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($address_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>"><?php echo $address; ?></textarea>
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $address_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($salary_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $salary; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $salary_err;?></span>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Submit">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
The same "create.php" file will display the HTML form and process the submitted form data. It will also perform basic validation on user inputs (line no-11 to 37) before saving the data.
Create Read Page
Now it's time to build the Read functionality of our CRUD application.
Let's create a file named "read.php" and put the following code inside it. It will simply retrieve the records from the employees table based the id attribute of the employee.
Example
<?php
// Check existence of id parameter before processing further
if(isset($_GET["id"]) && !empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Prepare a select statement
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
if($stmt = mysqli_prepare($link, $sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt, "i", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = trim($_GET["id"]);
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if(mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)){
$result = mysqli_stmt_get_result($stmt);
if(mysqli_num_rows($result) == 1){
/* Fetch result row as an associative array. Since the result set
contains only one row, we don't need to use while loop */
$row = mysqli_fetch_array($result, MYSQLI_ASSOC);
// Retrieve individual field value
$name = $row["name"];
$address = $row["address"];
$salary = $row["salary"];
} else{
// URL doesn't contain valid id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
mysqli_stmt_close($stmt);
// Close connection
mysqli_close($link);
} else{
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>View Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h1 class="mt-5 mb-3">View Record</h2>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["name"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["address"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["salary"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<p><a href="index.php" class="btn btn-primary">Back</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Check existence of id parameter before processing further
if(isset($_GET["id"]) && !empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Prepare a select statement
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
if($stmt = $mysqli->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bind_param("i", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = trim($_GET["id"]);
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
$result = $stmt->get_result();
if($result->num_rows == 1){
/* Fetch result row as an associative array. Since the result set
contains only one row, we don't need to use while loop */
$row = $result->fetch_array(MYSQLI_ASSOC);
// Retrieve individual field value
$name = $row["name"];
$address = $row["address"];
$salary = $row["salary"];
} else{
// URL doesn't contain valid id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
$stmt->close();
// Close connection
$mysqli->close();
} else{
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>View Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h1 class="mt-5 mb-3">View Record</h2>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["name"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["address"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["salary"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<p><a href="index.php" class="btn btn-primary">Back</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Check existence of id parameter before processing further
if(isset($_GET["id"]) && !empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Prepare a select statement
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = :id";
if($stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bindParam(":id", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = trim($_GET["id"]);
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
if($stmt->rowCount() == 1){
/* Fetch result row as an associative array. Since the result set
contains only one row, we don't need to use while loop */
$row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
// Retrieve individual field value
$name = $row["name"];
$address = $row["address"];
$salary = $row["salary"];
} else{
// URL doesn't contain valid id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
unset($stmt);
// Close connection
unset($pdo);
} else{
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>View Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h1 class="mt-5 mb-3">View Record</h2>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["name"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["address"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<p><b><?php echo $row["salary"]; ?></b></p>
</div>
<p><a href="index.php" class="btn btn-primary">Back</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Create Update Page
Similarly, we can build the Update functionality of our CRUD application.
Let's create a file named "update.php" and put the following code inside it. It will update the existing records in the employees table based the id attribute of the employee.
Example
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Define variables and initialize with empty values
$name = $address = $salary = "";
$name_err = $address_err = $salary_err = "";
// Processing form data when form is submitted
if(isset($_POST["id"]) && !empty($_POST["id"])){
// Get hidden input value
$id = $_POST["id"];
// Validate name
$input_name = trim($_POST["name"]);
if(empty($input_name)){
$name_err = "Please enter a name.";
} elseif(!filter_var($input_name, FILTER_VALIDATE_REGEXP, array("options"=>array("regexp"=>"/^[a-zA-Z\s]+$/")))){
$name_err = "Please enter a valid name.";
} else{
$name = $input_name;
}
// Validate address address
$input_address = trim($_POST["address"]);
if(empty($input_address)){
$address_err = "Please enter an address.";
} else{
$address = $input_address;
}
// Validate salary
$input_salary = trim($_POST["salary"]);
if(empty($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter the salary amount.";
} elseif(!ctype_digit($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter a positive integer value.";
} else{
$salary = $input_salary;
}
// Check input errors before inserting in database
if(empty($name_err) && empty($address_err) && empty($salary_err)){
// Prepare an update statement
$sql = "UPDATE employees SET name=?, address=?, salary=? WHERE id=?";
if($stmt = mysqli_prepare($link, $sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt, "sssi", $param_name, $param_address, $param_salary, $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_address = $address;
$param_salary = $salary;
$param_id = $id;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if(mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)){
// Records updated successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
mysqli_stmt_close($stmt);
}
// Close connection
mysqli_close($link);
} else{
// Check existence of id parameter before processing further
if(isset($_GET["id"]) && !empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// Get URL parameter
$id = trim($_GET["id"]);
// Prepare a select statement
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
if($stmt = mysqli_prepare($link, $sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt, "i", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = $id;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if(mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)){
$result = mysqli_stmt_get_result($stmt);
if(mysqli_num_rows($result) == 1){
/* Fetch result row as an associative array. Since the result set
contains only one row, we don't need to use while loop */
$row = mysqli_fetch_array($result, MYSQLI_ASSOC);
// Retrieve individual field value
$name = $row["name"];
$address = $row["address"];
$salary = $row["salary"];
} else{
// URL doesn't contain valid id. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
mysqli_stmt_close($stmt);
// Close connection
mysqli_close($link);
} else{
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Update Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5">Update Record</h3>
<p>Please edit the input values and submit to update the employee record.</p>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars(basename($_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'])); ?>" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($name_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $name_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<textarea name="address" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($address_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>"><?php echo $address; ?></textarea>
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $address_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($salary_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $salary; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $salary_err;?></span>
</div>
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo $id; ?>"/>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Submit">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Define variables and initialize with empty values
$name = $address = $salary = "";
$name_err = $address_err = $salary_err = "";
// Processing form data when form is submitted
if(isset($_POST["id"]) && !empty($_POST["id"])){
// Get hidden input value
$id = $_POST["id"];
// Validate name
$input_name = trim($_POST["name"]);
if(empty($input_name)){
$name_err = "Please enter a name.";
} elseif(!filter_var($input_name, FILTER_VALIDATE_REGEXP, array("options"=>array("regexp"=>"/^[a-zA-Z\s]+$/")))){
$name_err = "Please enter a valid name.";
} else{
$name = $input_name;
}
// Validate address address
$input_address = trim($_POST["address"]);
if(empty($input_address)){
$address_err = "Please enter an address.";
} else{
$address = $input_address;
}
// Validate salary
$input_salary = trim($_POST["salary"]);
if(empty($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter the salary amount.";
} elseif(!ctype_digit($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter a positive integer value.";
} else{
$salary = $input_salary;
}
// Check input errors before inserting in database
if(empty($name_err) && empty($address_err) && empty($salary_err)){
// Prepare an update statement
$sql = "UPDATE employees SET name=?, address=?, salary=? WHERE id=?";
if($stmt = $mysqli->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bind_param("sssi", $param_name, $param_address, $param_salary, $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_address = $address;
$param_salary = $salary;
$param_id = $id;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
// Records updated successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
$stmt->close();
}
// Close connection
$mysqli->close();
} else{
// Check existence of id parameter before processing further
if(isset($_GET["id"]) && !empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// Get URL parameter
$id = trim($_GET["id"]);
// Prepare a select statement
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
if($stmt = $mysqli->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bind_param("i", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = $id;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
$result = $stmt->get_result();
if($result->num_rows == 1){
/* Fetch result row as an associative array. Since the result set
contains only one row, we don't need to use while loop */
$row = $result->fetch_array(MYSQLI_ASSOC);
// Retrieve individual field value
$name = $row["name"];
$address = $row["address"];
$salary = $row["salary"];
} else{
// URL doesn't contain valid id. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
$stmt->close();
// Close connection
$mysqli->close();
} else{
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Update Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5">Update Record</h3>
<p>Please edit the input values and submit to update the employee record.</p>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars(basename($_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'])); ?>" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($name_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $name_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<textarea name="address" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($address_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>"><?php echo $address; ?></textarea>
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $address_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($salary_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $salary; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $salary_err;?></span>
</div>
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo $id; ?>"/>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Submit">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Define variables and initialize with empty values
$name = $address = $salary = "";
$name_err = $address_err = $salary_err = "";
// Processing form data when form is submitted
if(isset($_POST["id"]) && !empty($_POST["id"])){
// Get hidden input value
$id = $_POST["id"];
// Validate name
$input_name = trim($_POST["name"]);
if(empty($input_name)){
$name_err = "Please enter a name.";
} elseif(!filter_var($input_name, FILTER_VALIDATE_REGEXP, array("options"=>array("regexp"=>"/^[a-zA-Z\s]+$/")))){
$name_err = "Please enter a valid name.";
} else{
$name = $input_name;
}
// Validate address address
$input_address = trim($_POST["address"]);
if(empty($input_address)){
$address_err = "Please enter an address.";
} else{
$address = $input_address;
}
// Validate salary
$input_salary = trim($_POST["salary"]);
if(empty($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter the salary amount.";
} elseif(!ctype_digit($input_salary)){
$salary_err = "Please enter a positive integer value.";
} else{
$salary = $input_salary;
}
// Check input errors before inserting in database
if(empty($name_err) && empty($address_err) && empty($salary_err)){
// Prepare an update statement
$sql = "UPDATE employees SET name=:name, address=:address, salary=:salary WHERE id=:id";
if($stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bindParam(":name", $param_name);
$stmt->bindParam(":address", $param_address);
$stmt->bindParam(":salary", $param_salary);
$stmt->bindParam(":id", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_address = $address;
$param_salary = $salary;
$param_id = $id;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
// Records updated successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
unset($stmt);
}
// Close connection
unset($pdo);
} else{
// Check existence of id parameter before processing further
if(isset($_GET["id"]) && !empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// Get URL parameter
$id = trim($_GET["id"]);
// Prepare a select statement
$sql = "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = :id";
if($stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bindParam(":id", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = $id;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
if($stmt->rowCount() == 1){
/* Fetch result row as an associative array. Since the result set
contains only one row, we don't need to use while loop */
$row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
// Retrieve individual field value
$name = $row["name"];
$address = $row["address"];
$salary = $row["salary"];
} else{
// URL doesn't contain valid id. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
unset($stmt);
// Close connection
unset($pdo);
} else{
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Update Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5">Update Record</h3>
<p>Please edit the input values and submit to update the employee record.</p>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars(basename($_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'])); ?>" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name</label>
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($name_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $name_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address</label>
<textarea name="address" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($address_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>"><?php echo $address; ?></textarea>
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $address_err;?></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Salary</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control <?php echo (!empty($salary_err)) ? 'is-invalid' : ''; ?>" value="<?php echo $salary; ?>">
<span class="invalid-feedback"><?php echo $salary_err;?></span>
</div>
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo $id; ?>"/>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Submit">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">Cancel</a>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Create Delete Page
Finally, we will build the Delete functionality of our CRUD application.
Let's create a file named "delete.php" and put the following code inside it. It will delete the existing records from the employees table based the id attribute of the employee.
Example
<?php
// Process delete operation after confirmation
if(isset($_POST["id"]) && !empty($_POST["id"])){
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Prepare a delete statement
$sql = "DELETE FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
if($stmt = mysqli_prepare($link, $sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt, "i", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = trim($_POST["id"]);
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if(mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)){
// Records deleted successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
mysqli_stmt_close($stmt);
// Close connection
mysqli_close($link);
} else{
// Check existence of id parameter
if(empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Delete Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5 mb-3">Delete Record</h3>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]); ?>" method="post">
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo trim($_GET["id"]); ?>"/>
<p>Are you sure you want to delete this employee record?</p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Yes" class="btn btn-danger">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary">No</a>
</p>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Process delete operation after confirmation
if(isset($_POST["id"]) && !empty($_POST["id"])){
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Prepare a delete statement
$sql = "DELETE FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
if($stmt = $mysqli->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bind_param("i", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = trim($_POST["id"]);
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
// Records deleted successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
$stmt->close();
// Close connection
$mysqli->close();
} else{
// Check existence of id parameter
if(empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Delete Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5 mb-3">Delete Record</h3>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]); ?>" method="post">
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo trim($_GET["id"]); ?>"/>
<p>Are you sure you want to delete this employee record?</p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Yes" class="btn btn-danger">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">No</a>
</p>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<?php
// Process delete operation after confirmation
if(isset($_POST["id"]) && !empty($_POST["id"])){
// Include config file
require_once "config.php";
// Prepare a delete statement
$sql = "DELETE FROM employees WHERE id = :id";
if($stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql)){
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
$stmt->bindParam(":id", $param_id);
// Set parameters
$param_id = trim($_POST["id"]);
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if($stmt->execute()){
// Records deleted successfully. Redirect to landing page
header("location: index.php");
exit();
} else{
echo "Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
}
}
// Close statement
unset($stmt);
// Close connection
unset($pdo);
} else{
// Check existence of id parameter
if(empty(trim($_GET["id"]))){
// URL doesn't contain id parameter. Redirect to error page
header("location: error.php");
exit();
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Delete Record</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5 mb-3">Delete Record</h3>
<form action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]); ?>" method="post">
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?php echo trim($_GET["id"]); ?>"/>
<p>Are you sure you want to delete this employee record?</p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Yes" class="btn btn-danger">
<a href="index.php" class="btn btn-secondary ml-2">No</a>
</p>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Create Error Page
At the end, let's create one more file "error.php". This page will be displayed if request is invalid i.e. if id parameter is missing from the URL query string or it is not valid.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Error</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<style>
.wrapper{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2 class="mt-5 mb-3">Invalid Request</h3>
<div class="alert alert-danger">Sorry, you've made an invalid request. Please <a href="index.php" class="alert-link">go back</a> and try again.</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CRUD Operations in PHP and MySQL
How to Create a MySQL Database Connection?
To create a MySQL database connection in PHP:
First, you need to have a MySQL database installed and running.
You will also need the following information about your database:
Host name or IP address of the database server
Username and password to access the database
Database name that you want to connect to
Open a new PHP file in your code editor and start by creating a connection to the database using the mysqli_connect() function. The function takes four arguments:
Host name or IP address of the database server
Username to access the database
Password to access the database
Database name to connect to
Explanation:
In this example, we're connecting to a MySQL database on the same server as the PHP file, using the root user and an empty password. The database we're connecting to is called "mydatabase".
Test the connection by running the PHP file in your web browser. If the connection is successful, you should see the message "Connected successfully" on the page. If there's an error, you'll see an error message instead.
Let us see an image below:
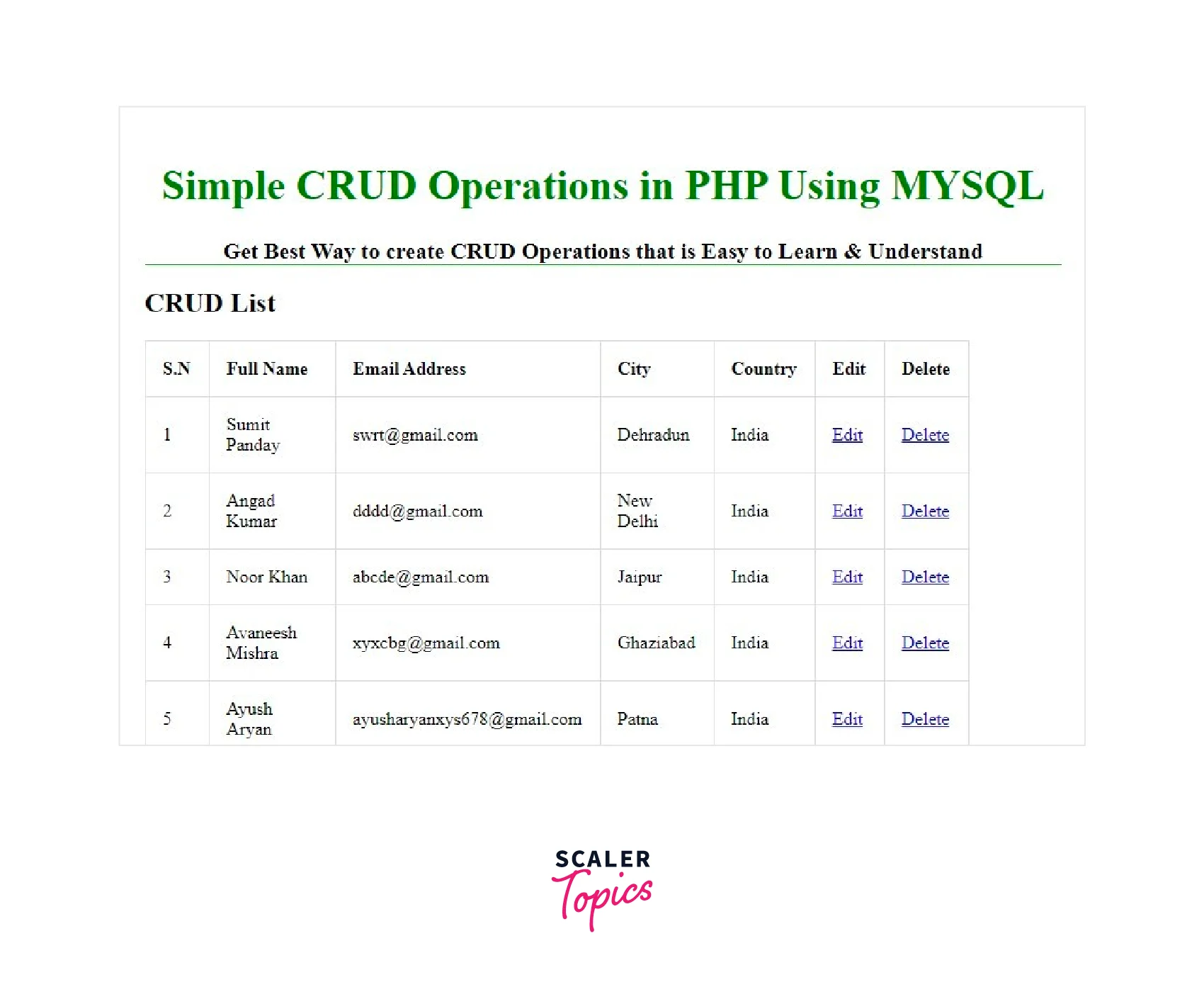
Create Records
To create records in PHP, you can use the PHP Data Objects (PDO) extension. PDO provides a consistent interface for working with different databases, including MySQL.
Connect to the database:
First, you need to establish a connection to the MySQL database using the mysqli_connect() function. This function takes the hostname, username, password, and database name as parameters.
Prepare the SQL statement:
Next, you need to prepare an SQL statement to insert the new record into the database. The SQL statement should include the table name and the column names where the data will be inserted.
Execute the SQL statement:
Once you have prepared the SQL statement, you can execute it using the mysqli_query() function.
Check for errors:
After executing the SQL statement, you should check if any errors were using the mysqli_error() function.
Close the database connection:
Finally, you should close the database connection using the mysqli_close() function.
By following these steps, you can create a new record in a MySQL database using PHP.
Read/View Records
To read/view records from a MySQL database using PHP, you can follow these steps:
Connect to the database using the mysqli_connect() function, as shown in the previous answer.
Write a SELECT query to retrieve the records you want to view. The query should be written in SQL and stored in a string variable in PHP. Here's an example:
This query selects all records from a table called "mytable".
Execute the query using the mysqli_query() function, passing in the database connection and the SQL query. Here's an example:
This will execute the query and store the result set in a variable called $result.
Loop through the result set using a while loop and the mysqli_fetch_assoc() function to retrieve each record as an associative array. Here's an example:
Explanation:
This code will loop through the result set and output the values of the "id", "name", and "email" columns for each record.
Close the database connection using the mysqli_close() function. Here's an example:
This will close the connection to the database.
Update Records
To update records in PHP and MySQL, you can follow these steps:
Connect to the MySQL database using the mysqli_connect() function. For example:
Prepare an SQL query to update the records in the database using the mysqli_query() function. For example:
Replace the "table_name" with the name of the table that you want to update, "column1" and "column2" with the names of the columns that you want to update, and "value1" and "value2" with the new values that you want to set.
Replace "some_column" with the name of the column that you want to use to identify the records that you want to update, and "some_value" with the value that you want to use to identify those records.
Execute the query using the mysqli_query() function.
Here's an example of how to update a record with a specific ID:
Explanation:
In this example, we're updating the "name" and "email" columns for the record with an ID of 1 in the "users" table.
It's important to check for errors after executing the query to ensure that the update was successful. You can use the mysqli_error() function to check for any errors that may have occurred during the update.
Delete Records
To delete records in PHP and MySQL, you can follow these steps:
Connect to the MySQL database using the mysqli_connect() function. For example:
Prepare an SQL query to delete the records from the database using the mysqli_query() function. For example:
Replace "table_name" with the name of the table that you want to delete records from.
Replace "some_column" with the name of the column that you want to use to identify the records that you want to delete, and "some_value" with the value that you want to use to identify those records.
Execute the query using the mysqli_query() function.
Here's an example of how to delete a record with a specific ID:
Explanation:
In this example, we're deleting the record with an ID of 1 from the "users" table.
It is very important to note that the DELETE statement in crud operation in php can be used to delete one or more records from a table based on specified criteria. For example, you can delete all records that meet a certain condition, such as all records where the "status" field equals "inactive".
In addition, it is very important to use caution while deleting all the records from the database because the operation can not be undone. Always make sure to double-check your criteria before executing a DELETE statement, and consider making a backup of your data before making any changes to your database.
Conclusion
Create operation in crud operation in php allows you to insert new records into the database using the mysqli_query() function.
Read operation in crud operation in php allows you to retrieve records from the database using the mysqli_query() function, and then loop through the result set using the mysqli_fetch_array() function to display the data.
Update operation in crud operation in php allows you to modify existing records in the database using the mysqli_query() function.
Delete operation allows you to remove records from the database using the mysqli_query() function.
Sanitizing user input is important to prevent SQL injection attacks, and prepared statements with placeholders should be used to achieve this.
It's important to establish a secure and reliable connection to the database before performing any CRUD operation.
Proper error handling and reporting should be implemented to catch any errors that may occur during the CRUD operation.
